Mission Details and Controlled Reentry
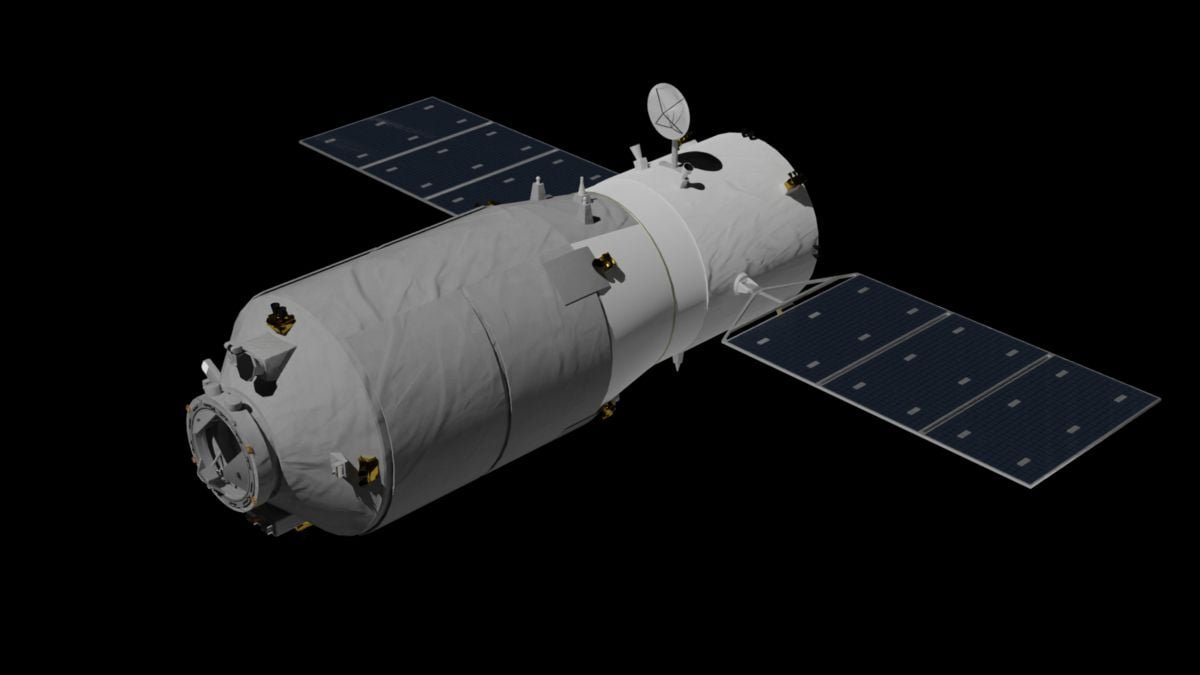
A Space.com report, quoting CMSA, revealed that Tianzhou 7 was undocked from Tiangong on November 10 after being loaded with waste from the station. The deorbiting course of was performed in a managed method, with the spacecraft’s engines fired to make sure its descent over the South Pacific Ocean, generally used for spacecraft reentry as a consequence of its remoteness. While CMSA launched visuals of Tianzhou 7’s atmospheric entry exhibiting intense flashes attributable to warmth and friction, particular particulars of the touchdown zone stay undisclosed.
Deployment of a Cubesat Pre-Reentry
Ahead of its managed descent, Tianzhou 7 reportedly launched a 6U cubesat named Bayi-08 on November 16. The satellite tv for pc, developed by the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), carries a medium-resolution Earth remark digital camera and an optical communication payload. It is a part of a science outreach programme aimed toward selling understanding of area expertise.
Operations at Tiangong Ongoing
While Tianzhou 7 concluded its mission, operations at Tiangong proceed. The report said that Tianzhou 8 was launched on November 15, carrying provides to maintain astronauts aboard the station. Preparations are additionally underway for the Shenzhou 20 mission, scheduled for spring 2025. The cargo included lunar soil simulant bricks for experimental functions and supplies to assist the Shenzhou.
China’s developments in its area programme stay a focus, with the Tiangong station taking part in a crucial position in supporting long-term human spaceflight and analysis aims.