Key Discoveries from Coprolite Analysis
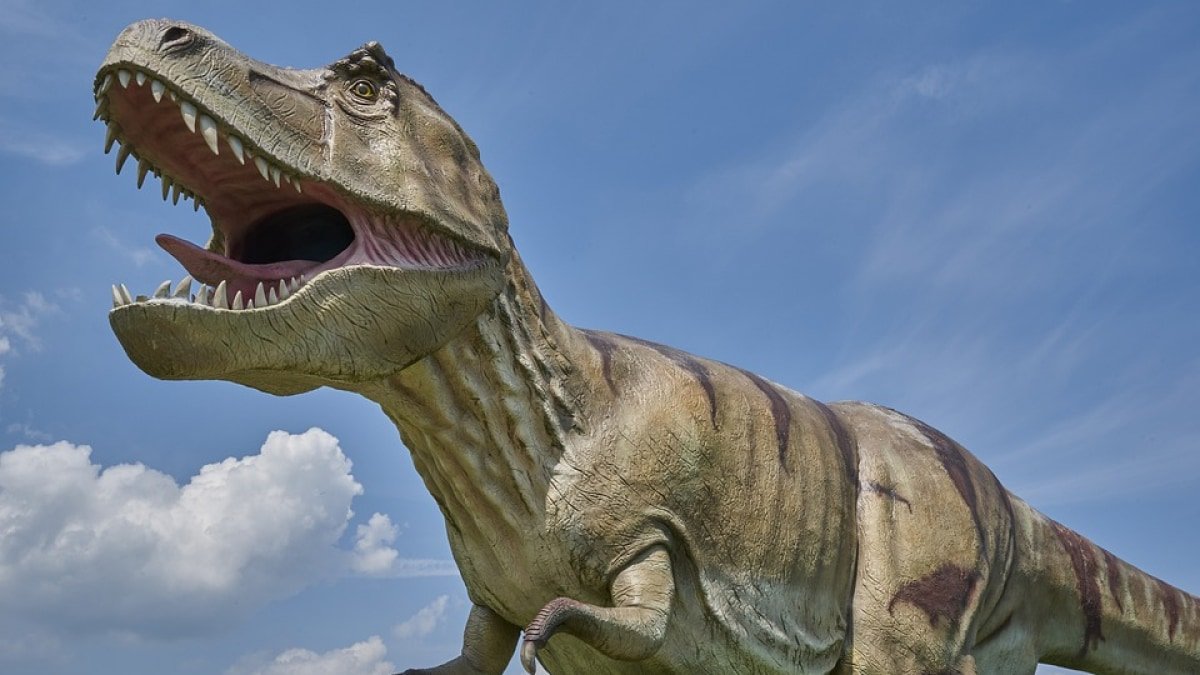
The research focussed on the northern areas of the supercontinent Pangea, with materials gathered over 25 years. Advanced imaging methods had been utilised to look at the interior constructions of coprolites, revealing well-preserved stays of fish, bugs, and bigger prey. Notably, proof was discovered of bones consumed and digested by predators into salts and marrow, mirroring behaviours noticed in species like hyenas at the moment.
Coprolites from herbivorous dinosaurs, akin to early sauropods, had been discovered to comprise tree ferns and different crops. Researchers had been intrigued by the invention of charcoal in these samples, suggesting these dinosaurs ingested it to neutralise toxins present in sure ferns.
Adaptability as a Survival Mechanism
In the examine, the dietary range of those early dinosaurs was highlighted as a big issue of their evolutionary success. Grzegorz Niedźwiedzki, co-author of the analysis, informed in a press release that the flexibility to adapt to altering environments by way of plant consumption was essential for his or her survival. According to the findings, these herbivorous dinosaurs displayed a desire for recent plant shoots, which enabled them to endure environmental upheavals in the course of the Late Triassic.
The examine contributes to understanding how adaptability in weight loss program and behavior allowed dinosaurs to thrive amidst climatic challenges, paving the best way for his or her dominance on the planet.