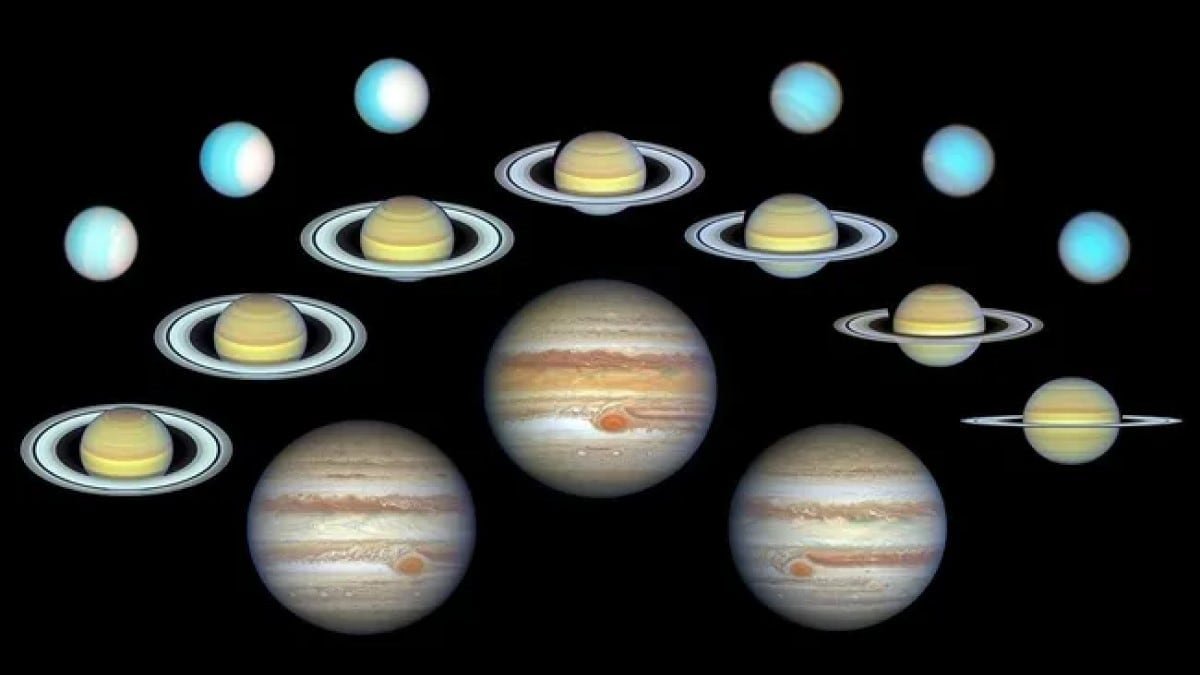
Jupiter’s Great Red Spot and Atmospheric Bands
The photo voltaic system’s largest planet, Jupiter, has revealed shifting options by way of the OPAL program. Reports point out modifications within the dimension and construction of the Great Red Spot, a colossal storm thrice the scale of Earth, and atmospheric phenomena inside its equatorial bands. According to NASA information, the planet’s minimal axial tilt of three levels ends in restricted seasonal variability, contrasting with Earth’s extra pronounced seasonal modifications brought on by a 23.5-degree tilt.
Saturn’s Seasonal Phenomena and Ring Activity
Reportedly, Saturn’s atmospheric circumstances, influenced by its 26.7-degree tilt, have been documented throughout its 29-year orbit. OPAL findings embrace color variations and cloud depth shifts correlating with the planet’s seasonal transitions. The telescope additionally captured the elusive darkish ring spokes, which, primarily based on information, are pushed by seasonal elements. Initially recognized throughout NASA’s Voyager missions, these phenomena now have clearer observational timelines on account of Hubble’s contributions.
Uranus’ Polar Brightness Increasing
With its excessive axial tilt and an 84-year orbit, Uranus has displayed gradual however noticeable modifications. According to analysis information, the northern hemisphere’s polar cap has brightened over time, aligning with its strategy to a summer season solstice anticipated in 2028. Hubble’s constant monitoring has enabled these long-term observations.
Neptune’s Storms and Solar Cycle Link
Neptune, the farthest of the 4, has revealed darkish storms, together with one first noticed in 2018 and one other documented in 2021. Based on OPAL evaluation, these storms dissipate close to the equator. Observations have linked Neptune’s atmospheric circumstances to the photo voltaic cycle, suggesting interconnected planetary climate influences. Reports point out that OPAL’s ten-year survey has enriched understanding, with findings shared in over 60 scientific publications.